Ever wonder about those old New Deal era records that were turned over to the National Archives by various government agencies for a Preliminary Inventory (PI) when their programs ended in 1942?
Ever wonder about those old New Deal era records that were turned over to the National Archives by various government agencies for a Preliminary Inventory (PI) when their programs ended in 1942?
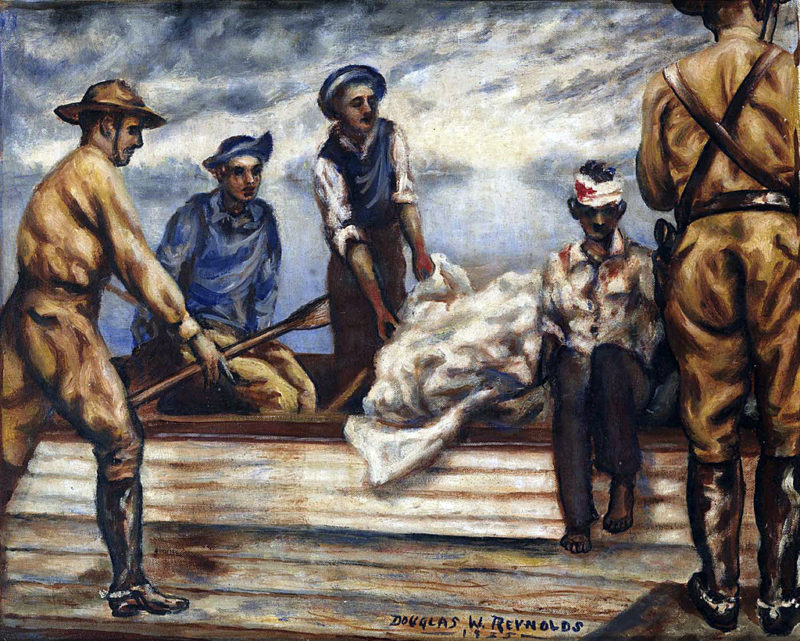
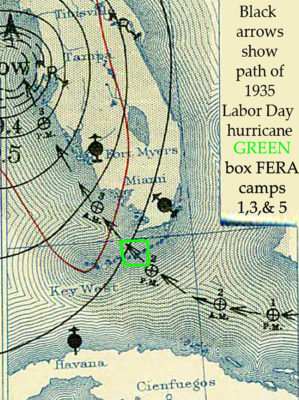
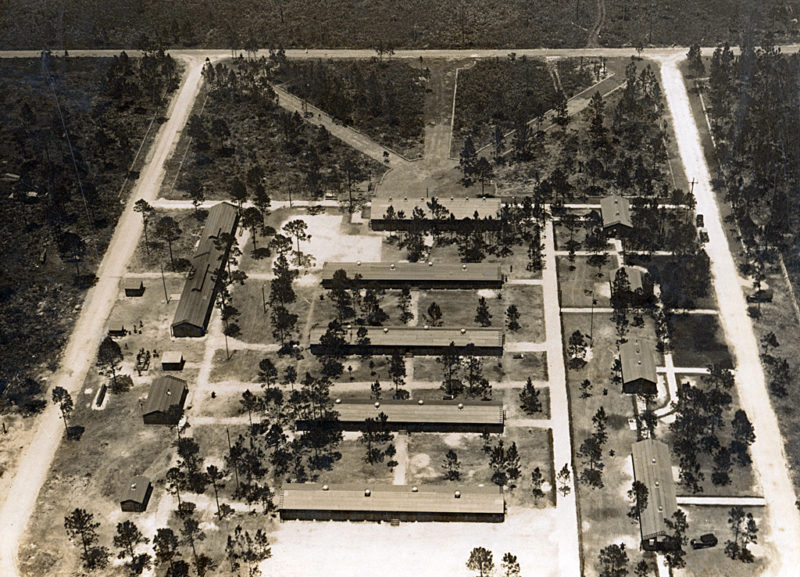
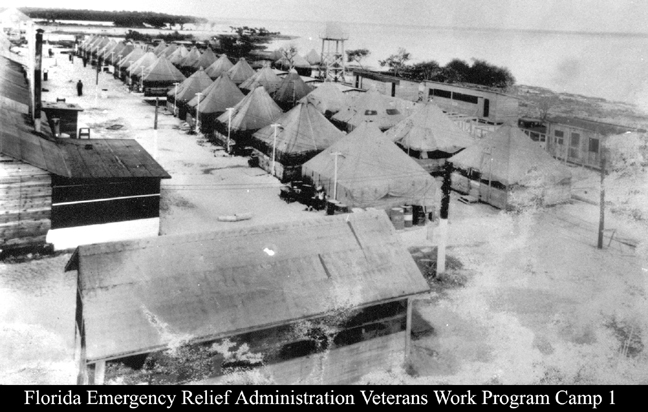
One of those vintage collections is Record Group (RG) RG35 containing agency Records of the Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC). The CCC was initially named Emergency Conservation Work (ECW); the program was commonly and later (1937) officially known as the Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC), the name under which they are cataloged.
The files in RG35 may be over nine decades old but they remain a fascinating and insightful collection of Great Depression documents, letters, appeals, CCC camp inspections, investigations, visuals and dispatches from the first, longest-lasting, and most popular of the 60 New Deal agencies, the CCC. They may be vintage, but they are far from forgotten by history enthusiasts, genealogists, and researchers alike.
New Deal Records Unavailable
In early November 2024, a research request was sent to the National Archives and Records Administration (NARA) in College Park, Maryland, for Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC) camp Inspection Reports found in Record Group RG 35. The reply was unexpected – the RG 35 stack is closed and slated to be moved to the NARA Federal Records Center in Kansas City, Missouri. Unfortunately, the records will be unavailable until 2025.
Disappointing? Yes. But there’s more to this story and the New Deal era collections.
What can be established is that thousands of New Deal era textual records, deemed inactive, will be stored offsite deep beneath the Kansas and Missouri prairies in one of NARA’s underground man-made limestone caves, much like the subterranean storage facility in Lenexa, Kansas pictured above. The caves are within driving distance of the Kansas City NARA and, good news for researchers, parking is free.
A complete listing of the RGs moving to the salt mines is listed on the NARA website titled “What’s New For Researchers” for October 2024.

The Custodial Why, How, and Where of New Deal Era Records
This news was confirmed in conversations with the acknowledged go-to source and expert for all things New Deal at the College Park NARA, Eugene Morris. What follows is the gist of our correspondence, beginning with:
“Gene, what’s happening?” Say it ain’t so. What Record Groups are moving in 2025? Is there a list?.. . Also, WPA, the work projects and art programs (microfilm, photographs & textural). Are the New Deal records being moved?
Gene answered …
It mostly has to do with the fact that the New Deal era records are mature, dead records (nothing new coming in). They don’t require a lot of additional work. They don’t have PII or restricted information.
- Stack 530* is being taken over by the Presidential Libraries unit, so everything in there has to move out, either elsewhere in the building or to KC. The New Deal cluster of records, RG 35 (CCC), RG 69 (WPA), RG 114, (NYA) and RG 135 (PWA) are all slated to move to KC. This will probably happen in the March to May of next year.
*Stack 530 is a very large room with 50+ rows of movable shelving in it. It’s being taken over by the Presidential Libraries unit to house records and items from the Trump and Biden administrations until their respective libraries/museums are up and running. Then it will continue to provide that service to subsequent administrations.- CCC records in other RG’s will still be here, like RG 79 (Park Service), RG 95 (Forest Service)… RG 407 and the little bit in RG 121.
- …the special media, the records in Still Pictures, Motion Pictures and Cartographics, will remain here in College Park.
- The records should only be closed for 6 to 8 weeks. The year I mentioned is the time it will take to get a staffer familiar enough with the records to do good reference work.
Some material in Stack 530 is not being moved to KC and is being moved to other stacks here. Because we’re so strapped for space, that means some records in those other stacks* will move to KC to make room for the records from Stack 530.
Building new buildings is expensive. Digging out a chunk of an old salt mine in suburban Kansas City and framing rooms inside is much cheaper. We have had “caves” in Lenexa and Lee’s Summit, Missouri for 25+ years. Both sites are roughly 30 minutes to an hour’s drive from our KC branch.
——————————-
New Deal records research will become more challenging. Perhaps, the National Archives’ ongoing digitization initiatives will prioritize these popular RG35 New Deal era records slated for the salt mines. As technology becomes available perhaps scans of these records will be considered for inclusion in their online catalog given its historical significance.
It stands to reason demand will grow for digital access to these and other archival New Deal records once the highly anticipated release of the digitized Civilian Conservation Corps Individual Records of Employment, Form No. 1 are freely uploaded and made available to the National Archives Catalog before the end of 2024.
The research and New Deal stories continue.
—————————-
NOTES:
Image: Lexana, Ks Federal Records Center, The National Archives Goes Underground, Spring 2016, Vol. 48, No. 1 | The Historian’s Notebook
By Jessie Kratz